Electronic Structure and Periodicity
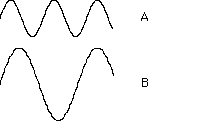
19. (Electromagnetic radiation, spectroscopy) Which wave
has a higher frequency?
A, B, both have the same frequency
21. (Electronic configuration) Mn: [Ar]4s2
3d? How many d electrons does Mn have?
4, 5, 6
22. (Electronic configuration, valence electrons) Which
electrons are most likely to be involved in chemical reactions?
those nearest to the nucleus, those farthest from the nucleus, all are
equally likely to be involved
23. (Ionic radius) Which is larger,
Na+ or Na?
Cl or Cl-?
24. (Valence electrons) How many valence electrons are
in Cl, [Ne]3s2 3p5?
2, 5, 7
For Cl to achieve a noble gas configuration, it is more likely that
electrons would be added, electrons would be removed
25. (Lewis dot structures, octet rule) What is a correct
Lewis dot representation of carbon monoxide?
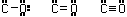
26. (Lewis dot structures, bonding) Compare O-O and O=O.
Is O=O expected to be
stronger, weaker, or the same strength?
Is O=O expected to be
longer, shorter, or the same length?
37. (Isoelectronic structures, periodic properties; Ch.
7 "Companion") Ge is a semiconductor. If half of the Ge atoms
of a sample of Ge are replaced with Ga atoms, with what element should the
other half of the Ga atoms be replaced in order for this new compound to
be isoelectronic with Ge?
Sn, As, Se
38. (Band gap energy, spectroscopy, semiconductors; Ch.
7 "Companion") Setup: Band gap energy has been introduced in a
localized picture: it can be defined as the energy needed to remove an electron
from a bond in the solid, enabling the electron to move freely through the
solid to conduct electricity. When itinerant electrons return to such a
one-electron bond, the band gap energy can be released as a photon. The
band gap energy is to a first approximation expected to increase as the
bonds become stronger and shorter and the electrons are held more tightly.
The group 14 elements illustrate this effect with diamond being an electrical
insulator, silicon and germanium (longer, weaker bonds in the same diamond
structure) being semiconductors, and ap;tin being a metal. Demonstration
7.11 "Companion": A trio of related predictions: what will
happen to interatomic spacing, band gap energy, and the color of the light
emitted when an orange LED is cooled in liquid nitrogen. On cooling,
atoms of the semiconductor will get closer together, atoms will get
farther apart
band gap energy increases, band gap energy decreases
color of light will become more red, color of light will become more yellow
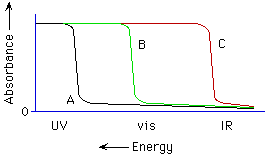
40. (Spectroscopy; Ch. 7 "Companion") Knowing
diamond is transparent, which curve best represents the absorption spectrum
of diamond (see below)?
A, B, C
41. (Superconductors, periodic properties; Ch. 9 "Companion")
A major research breakthrough was the discovery that an oxide of La, Cu,
and Ba was superconducting. When this material was "squeezed,"
the high pressure raised the critical temperature at which it became superconducting.
Given this effect, which element should be tried as a +3 ion replacement
for La to raise the critical temperature without having to apply pressure?
Hf, Y, Ac
51. (Solid solutions, periodic properties; Ch. 7 "Companion")
Which of the following is a reasonable solid solution?
GaxAl1-xAs, GaPxAs1-x, GaAlxAs1-x
55. (Energy diagrams) According to the energy diagram
below for the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, if an electron jumps from
E1 to E2, energy is
absorbed, emitted, not involved
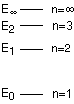
56. (Magnetism, unpaired electrons; Ch. 2 "Companion")
Two gel capsules, A and B, are filled with KMnO4 and MnO2,
respectively. Based on Mn formal oxidation state and numbers of unpaired
electrons, which will have a stronger attraction to a magnet?
A, B
Demonstration 2.2 "Companion": Fill one gel capsule
with KMnO4 (Mn+7, do), another with MnO2
(Mn+4, d3) and a third with Fe (or Co, Ni) powder. Bring a strong
magnet near and even touching the KMnO4 capsule. Note the lack
of any attraction. Repeat with the MnO2 capsule, which will be
weakly attracted to the magnet due to the unpaired electrons. The Fe capsule
will jump to the magnet illustrating the much stronger magnetic attraction
for the ferromagnetic material with its cooperative electronic interactions.
For large audiences, this demonstration can be done on an overhead projector.
57. (Transition metal complexes) Ti(H2O)63+
has how many d-electrons?
d0, d1, d2
With regard to magnetic properties, Ti(H2O)63+
is
paramagnetic, diamagnetic?
Ti(H2O)63+ absorbs yellow light. Based
on complementary color relationships (color wheel), what color does it appear?
red, green, violet
58. (d-orbitals) Co2+ has seven electrons in
its d-orbitals, which are split as shown below in octahedral coordination
geometry. In a high spin configuration, how many electrons are unpaired?
1, 2, 3
In a low spin configuration, how many electrons are unpaired?
1, 2, 3
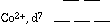
67. (Spectroscopy, probability; Ch. 8 "Companion")
If a blue cupric solution cuts the amount of red laser light reaching a
solar cell, which counts photons as photocurrent, in half...
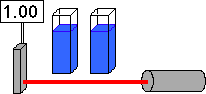
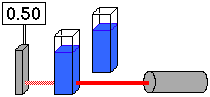
...what will happen if a second solution is added?
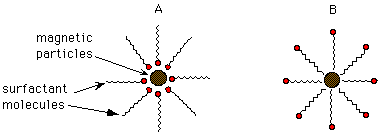
79. (Magnetism, polarity, surfactants; Ch. 2 "Companion,"
Demonstrations 2.6, 2.7) In a ferrofluid preparation, the intent is to keep
magnetic particles suspended in an oily medium. How do the surfactant molecules
interact with this medium?
A, B
83. (Doping, semiconductors, periodic properties; Ch.
8 "Companion") Which dopant will act as an acceptor for Si?
B, Ge, As
As a donor?
B, Ge, As
95. (Spectroscopy) Demonstration: The current measured
in the set-up below is 2 mA. If the sealed sample cell containing a light-absorbing
solution is turned lengthwise, what current will be measured?
>2 mA, =2 mA, <2 mA
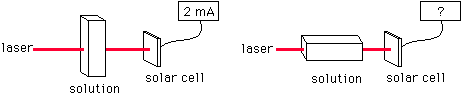
96. (Transition metal complexes) For octahedral complexes,
which metal ion fills the 3d subshell with electrons?
Ni2+, Cu2+, Zn2+

What color is predicted based on the possible d-d transitions of this
complex?
white, red, black
103. (Band gap energy; Ch. 7 & 8 "Companion")
For promoting electrons to the conduction band and forming e--h+ pairs,
which photons are the most energy efficent?
hv>Eg, hv=Eg, hv<Eg
109. (Semiconductors; Ch. 7 "Companion") A CdS
photocell measures light intensity by its change in resistance. If the intensity
of light increases, the CdS resistance
increases, decreases, stays constant
115. (Electronegativity, bonding, band gap energy; Ch.
7 "Companion") The atoms below have the following electronegativities:
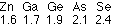
The three isoelectronic semiconductors Ge, GaAs, and ZnSe all have roughly
the same size unit cell and internuclear separation (exclusively Ge-Ge,
Ga-As, and Zn-Se bonds, respectively). If under these conditions, band gap
energy increases with ionic character, which isoelectronic solid should
have the largest band gap energy?
Ge, GaAs, ZnSe
119. (Coordination chemistry) Consider the complex CrF63-
with anionic F- ligands. What is the formal oxidation state of the chromium?
3, 0, -3
120. (Coordination chemistry) Which of the following are
isoelectronic with the H2O molecule, which commonly serves as
a ligand?
methane CH4, ammonia NH3, fluoride F-
Which of the above could serve as a ligand if lone pairs are required for
binding to the metal center?
methane CH4, ammonia NH3, fluoride F-




More questions are needed for this section. Please submit contributions
to concept@chem.wisc.edu..


![]()

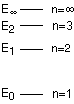




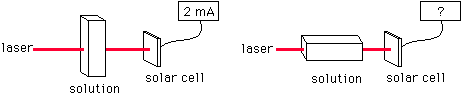
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()