Chemical Reactions,
Acid-Base, Redox, Precipitation
13. (Acids and bases, amphoterism) Demonstration:
Three Petri dishes are partially filled with concentrated NaCl solution,
concentrated NaOH solution and concentrated HCl solution and placed on an
overhead projector. A small piece of aluminum foil is added to each dish.
Reaction occurs in the solutions of HCl and NaOH. Which ions appear to react
with the Al metal based on this experiment? (The observed induction period
with base can also be used to discuss the thin coating of aluminum oxide
that must first be dissolved for the reaction with base to occur.)
Na+, OH-, Cl-, H+
14. (Redox) Cu(s) + 1/2 O2 (g) ---> CuO
(s)
The oxidation number of copper in the product is
Cu(0), Cu(I), Cu(II)
In the reaction, copper metal is
reduced, oxidized, unchanged in oxidation state
15. (Limiting reagents, precipitation, solubility) Demonstration:
A solution of Ba(NO3)2 is added to a solution of Na2SO4
to make a precipitate. From a table of solubility rules, the product is
barium sulfate, sodium nitrate
The amount of precipitate collected from the fixed amount of Na2SO4
solution as the Ba(NO3)2 is added indefinitely will
look like which graph below?

A, B, C
The break point of the graph will occur when the ratio of moles of Ba2+
to moles of SO42- is
1:1, 1:2, 2:1
52. (Solid-state synthesis, solid solutions; Ch. 3 &
10 "Companion") Which synthetic methods would intimately mix Si
and Ge on the atomic scale to create SixGe1-x solid solutions?
co-grinding, co-melting and condensing, co-vaporizing and condensing
68. (pH scale) A solution with pH=5 is 100 times more
acidic than a solution with a pH =?
7, 3, 0.05
69. (Weak acids) In acetic acid, pictured below, from
where will the H+ come?
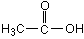
O-H or C-H
70. (Weak acids, Le Châtelier's principle) CH3COOH
= CH3COO- + H+; pKa=5
To make more CH3COOH, add
NaOH, HCl
To make more CH3COO-, add
NaOH, HCl
At pH=2, what is the most prevalent species?
CH3COOH, CH3COO-, equal amounts of the acid and
its conjugate base
At pH=5, what is the most prevalent species?
CH3COOH, CH3COO-, equal amounts of the acid and
its conjugate base
Which plot shows the correct distribution of acetic acid as a function
of pH?
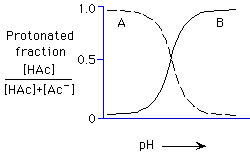
A, B
72. (Amino acid sequences) Amino acids are joined by peptide
bonds formed through condensation reactions. Is the compound gly-ala the
same as ala-gly?
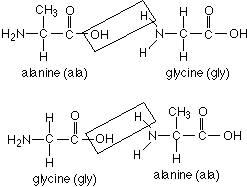
yes, no
75. (Polymers, thermodynamics) Consider the polymerization
of ethylene in which, neglecting the ends of the polymer, many C=C double
bonds worth ~600 kJ/mol each are converted to twice as many C-C single bonds
in polyethylene worth ~350 kJ/mol each.
n H2C=CH2 (g) --> -[-CH2-CH2-]-n
This reaction is
exothermic, endothermic, thermoneutral
What happens to the entropy in this reaction?
increases, decreases, remains the same
100. (pH scale) Demonstration: Predict a pH value for
0.1 M NaOH.
1, 7, 13
101. (Buffers) When adding acid to an acetate buffer,
H+ reacts with
CH3COOH, CH3COO-
105. (Reaction profiles) Considering the reaction profile
below, the activation energy is larger when the reaction proceeds in which
direction?
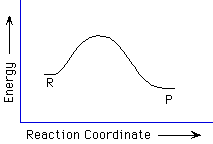
forward, reverse, equal
106. (Photosynthesis) O2 + [CH2O]
<---> CO2 + H2O + energy
carbohydrate
Does the forward or reverse reaction represent photosynthesis?
forward reaction, reverse reaction
123. (Acids and bases, indicators) Demonstration:
Strong base is added to a solution containing methyl red indicator, giving
a red color; adding strong acid gives a yellow color. The deprotonated form
of the methyl red indicator is
yellow, red
135. (Acids and bases, pH scale) Demonstration:
The pH of 90 mL of a 0.1 M solution of HCl is measured with a digital pH
meter and shown to be about 1. Roughly how many mL of water need to be added
to reach a pH of about 2?
10, 100, 1000
146. (Ions) Solutions of NaNO3 and K2SO4
are dissolved in water and the water then allowed to evaporate. How many
possible salts could be recovered?
2, 3, 4
178. A beaker contains 100 mL of salt water. If 100 mL
of distilled water is added to the beaker, the number of moles of NaCl
increases by 50%, decreases by 50%, doesn't change
186. To prepare nickel (II)
sulfate by combining two reagents and evaporating the resulting solution
to dryness, which pair of reagents would you use?
Ni(NO3)2(aq) and Na2SO4(aq)
Ni(OH)2(s) and H2SO4(aq)
187. Identify the oxidizing
agent in the reaction:
2Al(s) + 6 H+(aq) ==> 2 Al3+(aq) + 3 H2(g)
Al, H+, Al3+, H2
198. In the following reaction,
which species is acting as an acid?
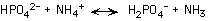
HPO42-, NH4+
199. Which of the following will
act as a Lewis Acid?
PH3, AlCl3, HCN
200. What concentration of HNO3
must be added to water to make [OH-] = 10-9M?
10-9 M, 10-5 M, 10-1 M
201. Which of the following "molecular"
pictures best represents a concentrated solution of the weak acid HA with
Ka = 10-5?
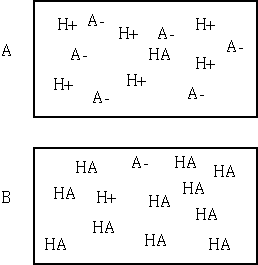
A, B
202. When dissolved in water,
which of the following salts will produce a basic solution?
KF, KNO3, NH4NO3
203. What is the correct expression
for the solubility product constant for Mg3(PO4)2?
Ksp = [Mg2+] [PO43-]
Ksp = [Mg2+]2 [PO43-]3
Ksp = [Mg2+]3 [PO43-]2
228. The extent of ionization of a drug helps
determine how it is distributed in the body because ions are less likely
to cross cell membranes than uncharged molecules than uncharged molecules.
Where is aspirin, an organic acid, readily absorbed in the body?
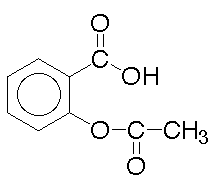
Asprin
A. In the acid environment of the stomach
B. In the basic environment of the intestine
229. The extent of ionization of a drug helps determine
how it is distributed in the body, because ions are less likely to cross
cell membranes than uncharged molecules. Where are amphetamines readily
absorbed in the body?
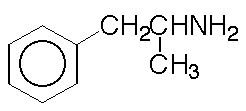
Amphetamine
A. In the acid environment of the stomach
B. In the basic environment of the intestine
231. The pH of blood is maintained by the bicarbonate
buffer system through the amount of CO2 in the blood.
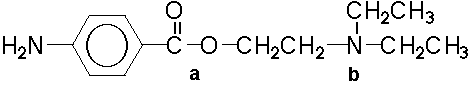
How will the pH change with hyperventilation, during which the concentration
of CO2(aq) decreases?
228. The extent of ionization of a drug helps
determine how it is distributed in the body because ions are less likely
to cross cell membranes than uncharged molecules than uncharged molecules.
Where is aspirin, an organic acid, readily absorbed in the body?

Asprin
A. In the acid environment of the stomach
B. In the basic environment of the intestine
229. The extent of ionization of a drug helps determine
how it is distributed in the body, because ions are less likely to cross
cell membranes than uncharged molecules. Where are amphetamines readily
absorbed in the body?

Amphetamine
A. In the acid environment of the stomach
B. In the basic environment of the intestine
231. The pH of blood is maintained by the bicarbonate
buffer system through the amount of CO2 in the blood.
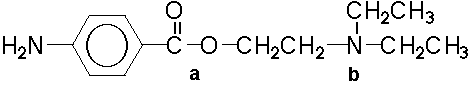
How will the pH change with hyperventilation, during which the concentration
of CO2(aq) decreases?
A. increase
B. decrease
C. no change



More questions are needed for this section. Please submit contributions
to concept@chem.wisc.edu..


![]()



![]()



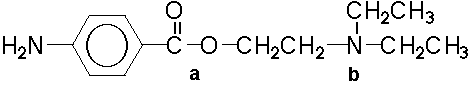


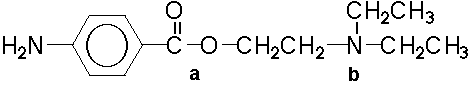
![]()
![]()
![]()