
Laves' Principle: The most stable structure for a solid is one in which the most efficient use is made of space. When a compound forms a crystalline solid, its atoms, ions, or molecules pack as closely as possible.
As we consider packing of spherical atoms, we will first consider how spheres of equal size (as in a metal) pack efficiently in a plane. Then we will consider how these planes can stack to fill space.
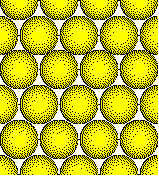
The
atoms in crystalline solids fill space as efficiently as possible.
This close packed arrangement of atoms is
typical of a metal.
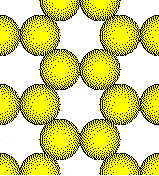
This open arrangement of atoms is unknown in a metal.
Copyright ©
2003
by: Journal of Chemical Education Software
by: Journal of Chemical Education Software